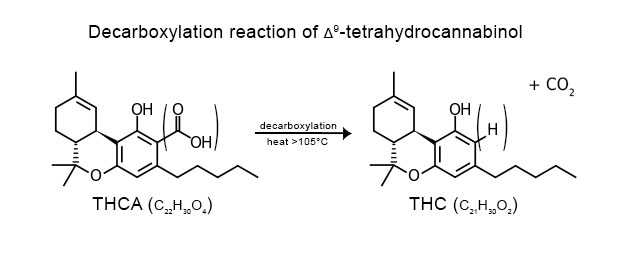
Growing or freshly harvested cannabis has little to no THC, instead having THCA (THC acid). Research suggests that while THCA has some anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects - it does not have the same substantial medicinal effects as THC. Nor the psychoactive effects. THCA does not get one high.
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that releases carbon dioxide via its carboxylic group (COOH). This means a chemical reaction takes place in which carboxylic acids loose a carbon atom from a carbon chain. This process converts THCA to THC - making the cannabis "active." When cannabis drys, it also very very slowly begin decarboxylation and converts THCA to THC. (THC will eventually degrade further to CBN.) We can speed the THCA-->THC process by simply heating dried cannabis to the correct temperature for enough time - thus releasing carbon dioxide and creating THC.
Why have so many of you never heard of this before? Decarboxylating also takes place without extra effort when cannabis is heated during the act of smoking or vaporizing, although the process can be imperfectly efficient. It also takes place to some degree when cannabis is cooked into butter or when hash and kief are added to a favorite recipe and then cooked in the oven. But both processes can be quite ineffecient, so you want to decarboxylate your cannabis before you vape it, eat it or make it in to tincture.
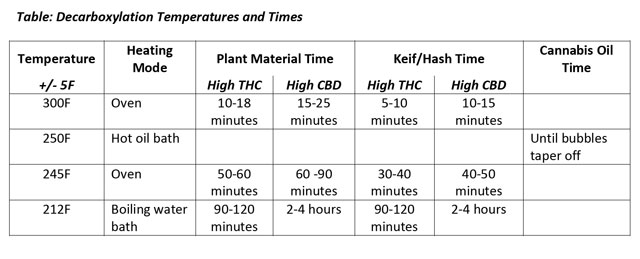
The goal of cannabis decarbing is to activate the cannabinoids with minimal evaporation of cannabinoids or terpenes (compounds responsible for how cannabis smells). The lower the temperature, the longer the decarb time required, but less loss of terpenes due to evaporation. Since terpenes are medicinal elements finding a happy medium is quite important.
The boiling points, and hence the vapor point of the major cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids ranges from 246.2° to 435.2° Fahrenheit. Therefore for best results you want to keep your heat below 246.2° F. Consumer grade ovens are not always exact so use a thermometer and shoot for a decarboxylation temperature of around 225° to 240° Fahrenheit. This should produce quick results without losing any medicinal potency.
An alternative method: use a boilable pouch bag - seal your cannabis inside and submerge the pouch in boiling water for at least an hour.