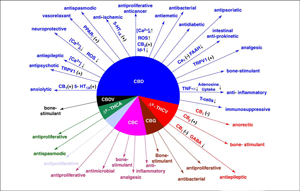
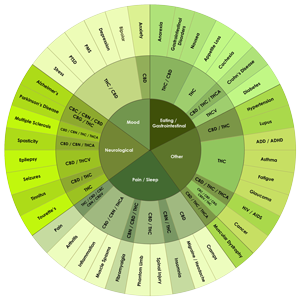
Cannabis contains up to 85 different cannabinoids (CBS), and potentially more than 200 terpenes and up to 23 flavonoids. Each of these classes of compounds contributes to its medicinal effects in what has been termed the "entourage effect." by Dr. Raphael Mechoulem the discoverer of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) the main psychoactive ingredient. The active chemicals responsible for the medicinal effects of cannabis are collectively called cannabinoids. This group includes THC, Cannabidiol (CBD), and Cannabinol (CBN). And again both terpenes and flavonoids also add to these medicinal effects. What we call cannabis strains are considered to be subspecies of cannabis with specific cannabinoid and terpene ratios - in other words the specific active ingredients mapped out like a fingerprint. The absolute levels of terpenes seem to vary somewhat with environmental factors such as water content, soil type, nutrient, light, temperature, etc. Modern cultivation methods enable production of strains with somewhat consistent ratios of terpenes to cannabinoids. How cannabis is grown also effects the cannabinoids and terpene ratios, the variability reflected in the fact cannabis is neither completely wild nor completely domesticated in the approximately 12,000 years we have been cultivated it.
Read more on the Entourage EffectTetrahydrocannabinol THC
THC acts on the central nervous and immune systems of humans. It is
the primary psychotropic ingredient in Cannabis, or the one that produces most of the high. While these psychotropic
effects have therapeutic benefits, THC also acts as a neuroprotective, analgesic painkiller, anti-inflammatory and anti-microbal and anti-bacterial
(microorganisms e.g., bacteria) agent. THC is also anti-cancer, anti-spasmotic, and an appetite stimulant and a bronchodilator. All THC starts as THCA in the plant which must release its COOH molecule in order to be active. This is called decarboxylation.
Cannabidiol CBD
Cannabidiol does not interact with the human body like other cannabinoids, but has significant therapeutic effects. CBD is a deep muscle relaxant. It appears to relieve anxiety, convulsion, depression, inflammation and nausea. Mildly psycho-active, it is also believed to moderate psychotic side effects of THC, such as schizophrenia-like symptoms. While unproven, CBD may exhibit anti-cancer activity, especially in breast cancer. It has mildly sedative effects. CBD has affinity for serotonin receptors which are associated with psychological well being.
Cannabinol CBN
Cannabinol is primarily produced by THC degrading. It is only mildly psychoactive but is also associated with greater disorientation. CBN is also produced by poor storage or transportation methods, when the plant trichomes are damaged. It is not desirable to have high levels of CBN In your medicinal product. Fresh cannabis contains little or no CBN.
Cannabigerol CBG
Cannabigerol (CBG) is called the “parent” cannabinoid because it is the chemical precursor of the acidic forms of THC, CBC and CBD. While its biological action is not completely understood, CBG is believed to be a painkiller, muscle relaxant and anti-erythemic (redness of skin, often a sign of inflammation or infection). It is also being investigated for potential anti-cancer activity. It is also analgesic, anti-microbial, anti-bacterial, anti-cancer, anti-depressant, anti-fungal and a bone stimulant. It is more powerful than THC as a pain killer.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin THCV
Tetrahydrocannabivarin is varient of but nearly identical to THC. It is found in some Asian and African strains where it can be as high as 16%. THCV appears to be less psychoactive than THC but cannabis with THCV in it is generally considered very potent. THCV acts on the human nervous and immune systems. It has strong anti-obesity properties and aids in memory. It is also an anti-convulsive, appetite supressant and a bone stimulant. Cannabis strains with considerable THCV are in demand by those doing cannabinoid research, as it might be medicinally stronger version of THC with a less noticable high.
Cannabidivarin CBDV
Little is known about Cannabidivarin (CBDV) as it is uncommon in modern varieties of Cannabis. Cannabis chemotypes which express CBDV are relatively rare and should be monitored closely. CBDV is anti-convulsive and a bone stimulant.
Cannabichromene CBC
Cannabichromene (CBC) is an anti-inflammatory and an analgesic. It is believed to be inactivein pure form but enhances THC. It is found in higher concentrations early in the lifecycle of a Cannabis plant and has been shown in to reduce THC intoxication in mice. It is analgesic, anti-bacterial, anti-cancer, anti-depressant, anti-fungal, anti-inflammatory, anti-insomnia, and a bone stimulant.
Myrcene
Myrcene is another terpene present in numerous cannabis varietals, is a sedative, a muscle relaxant, a hypnotic, an analgesic (painkiller) and an anti-inflammatory compound. This musky terpene contributes mightily to the infamous “couch-lock” experience, Russo maintains. Myrcene may act in synergy with THC, with their combined molecules creating a stronger effect than THC alone. This may be due to myrcene’s influence on the permeability of the cell membrane, which allows more THC to reach the brain. Myrcene blocks the effects of pro-mutagens implicated as carcinogens, such as aflotoxin B, and small amounts are found in essential oils associated with anti-depressive and moodenhancing effects.
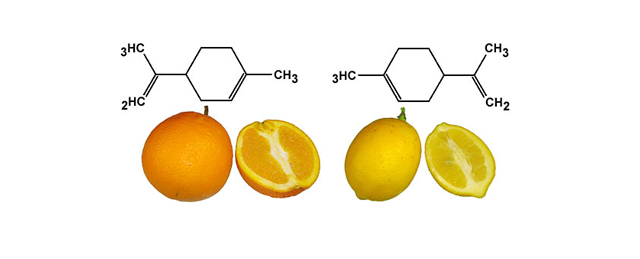
Limonene
Limonene, a major terpene in citrus as well as in cannabis, has been used clinically to dissolve gallstones, improve mood and relieve heartburn and gastrointestinal reflux. Limonene has been shown to destroy breast-cancer cells in lab
experiments, and its powerful antimicrobial action can kill pathogenic bacteria.
(Super Lemon Haze, anyone?)
Beta-Caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene is a sesquiterpene found in the essential oils of black pepper, oregano and other edible herbs, as well as in cannabis and many green, leafy vegetables. It is gastro-protective, good for ulcers, and shows great promise as a therapeutic compound for inflammatory conditions and autoimmune disorders because of its ability to bind directly to the peripheral cannabinoid receptor known as CB2. Caryophyllene is with what drug sniffing dogs were trained. It also lightens moods and enhances sociability.
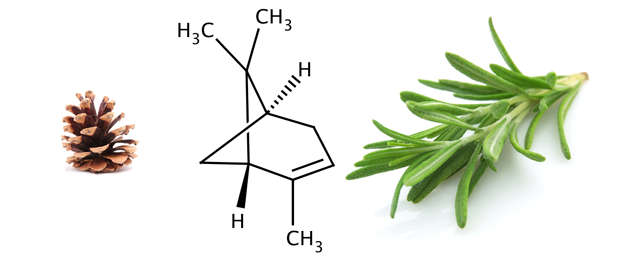
Terpene: Alpha-Pinene
Alpha-pinene (essential pine oil), the most common terpene in the plant world and one often found in cannabis, is a bronchodilator potentially helpful for asthmatics. Pinene also promotes alertness and memory retention by inhibiting the metabolic breakdown of acetylcholinesterase, a neurotransmitter in the brain that stimulates these cognitive effects. It is antibiotic and antimalarial.
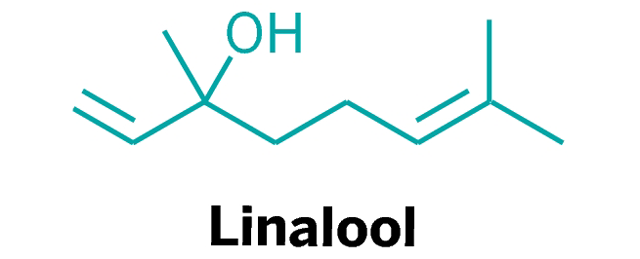
Terpene: Linalool
Linalool, a terpenoid prominent in lavender as well as in some cannabis strains, is an anxiolytic compound that counters anxiety and mediates stress. Linalool is a powerful sedative if inhaled. In addition, linalool is a strong anticonvulsant, and it also amplifies serotonin receptor transmission, conferring an antidepressant effect. Applied topically, linalool can heal acne and skin burns without scarring. Linalool is also found in lavender and roses.